Hey there! In this article, I’m going to take you on a journey into the heart of your beloved vehicle – the car engine. We’ll explore the basics of how car engines work in New Zealand, breaking down complex concepts into simple, easy-to-understand terms. So buckle up, because we’re about to dive into the fascinating world of car engines!
Key Takeaways:
- Car engines in New Zealand operate on the principles of internal combustion, where fuel is burned inside the engine to generate energy.
- Understanding how a car engine works is crucial for vehicle owners to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Components such as the cylinder block, crankcase, pistons, and camshafts all play specific roles in the engine’s operation.
- The lubrication system and oil filter are essential for keeping the engine properly lubricated and free from contaminants.
- By grasping the basics of a car engine, you’ll be better equipped to maintain and care for your vehicle.
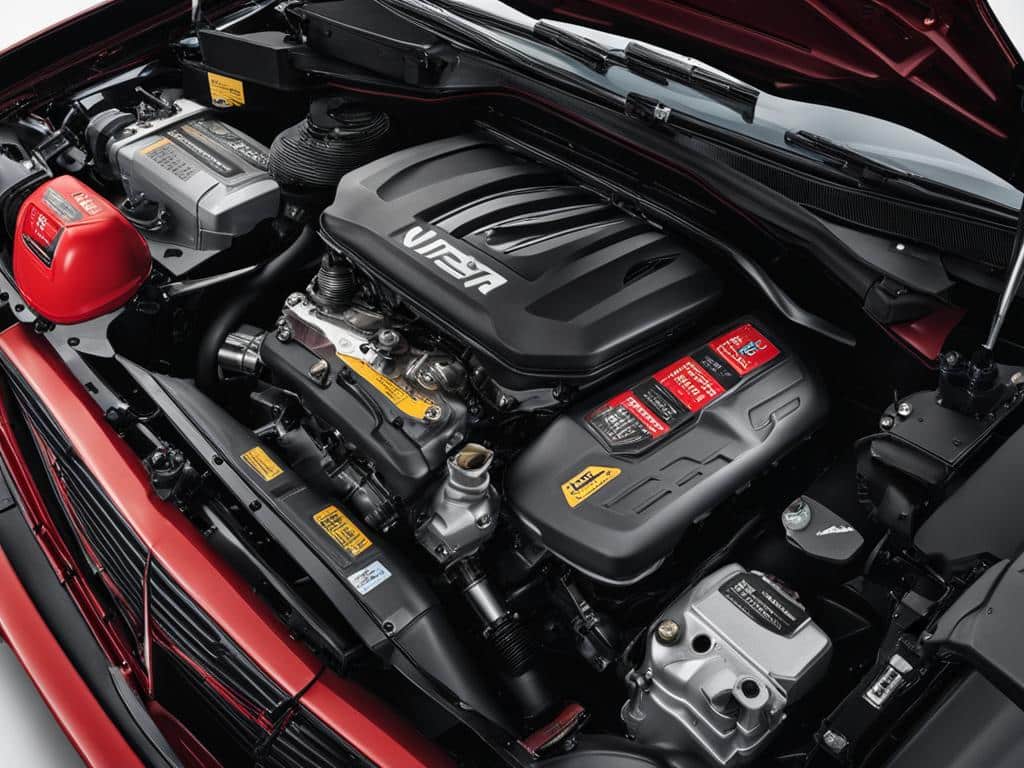
Car Engine Parts and Functions with Pictures
The car engine is a complex assembly of various components that work together to power the vehicle. Understanding the different parts and their functions is essential for maintaining and troubleshooting the engine. In this section, we will explore the key components of a car engine, accompanied by informative pictures to aid comprehension.
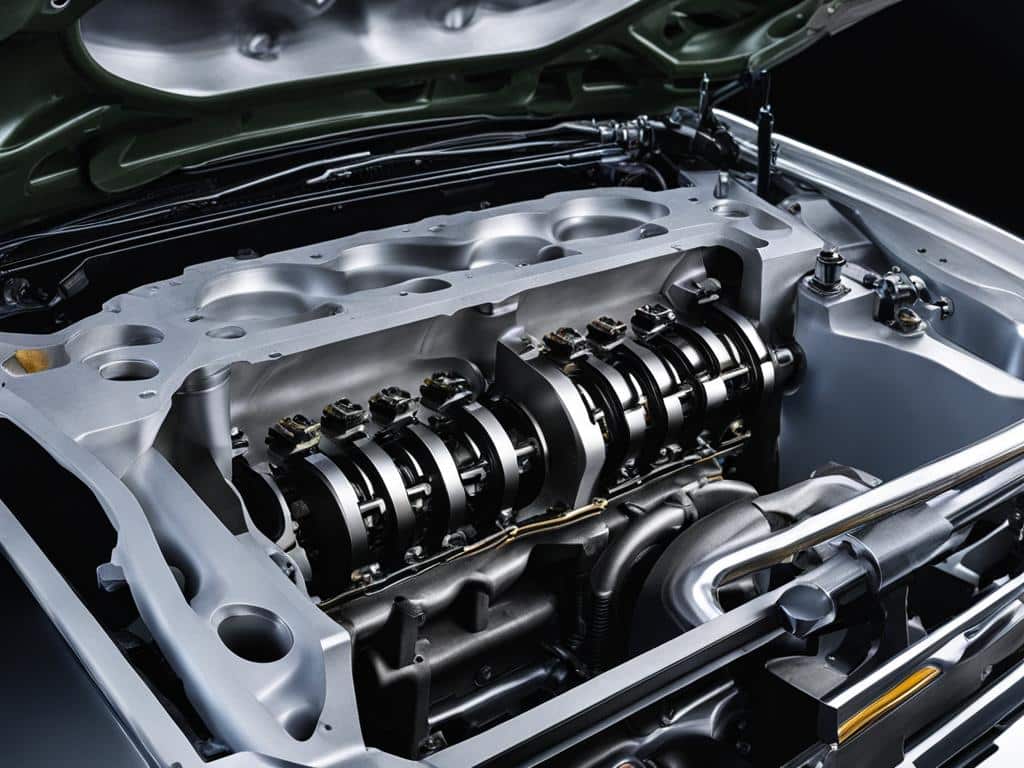

These two components, the cylinder block and cylinder head, form the core of the engine’s structure and function. They work hand in hand to ensure efficient combustion, power production, and overall engine performance. Without them, the engine simply wouldn’t operate.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the cylinder block and cylinder head, let’s move on to exploring other vital engine components in the upcoming sections.
Crankcase and Oil Pan
The crankcase and oil pan are integral components of a car engine’s lubrication system. The crankcase, located at the bottom of the cylinder block, houses the crankshaft and provides support for its main journals and bearings. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the alignment of these components under varying engine loads. The oil pan, also known as the sump, is attached to the crankcase and serves as a reservoir for engine lubricating oil.
One of the primary functions of the crankcase is to provide a stable environment for the crankshaft to operate. The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which in turn drives the wheels of the vehicle. The crankcase ensures that the crankshaft remains properly aligned and supported, reducing friction and wear on the crankshaft and bearings. It is designed to withstand the forces generated during engine operation and maintain the structural integrity of the engine.
The oil pan, on the other hand, collects and stores the lubricating oil that is vital for the smooth operation of the engine. The oil pan is strategically positioned below the crankshaft to allow gravity to assist in the flow of oil. It also acts as a cooling chamber for the oil, dissipating heat generated during engine operation. Additionally, the oil pan contains an oil pump pickup tube that draws oil into the pump, ensuring a constant supply of lubrication to all engine components.
Engine lubrication is crucial for reducing friction and wear, which can lead to costly engine damage. The crankcase and oil pan work together to provide a secure housing for the crankshaft and a reservoir for engine oil. Regular maintenance, including oil changes and inspections, helps ensure that the crankcase and oil pan perform their vital functions effectively, promoting the longevity and performance of the engine.
Manifolds and Gaskets
Manifolds and gaskets play crucial roles in the operation of a car engine. Engine manifolds, including the intake and exhaust manifolds, are responsible for the proper flow of air-fuel mixture and exhaust gases. The intake manifold carries the air-fuel mixture from the carburetor or fuel injector to the cylinders, while the exhaust manifold transports the exhaust gases from the cylinders to the exhaust system. The design of the manifolds is critical to ensure efficient combustion and optimal performance of the engine.
Gaskets, on the other hand, are essential for creating a tight seal between two mating surfaces, such as the cylinder head and block or the manifold and engine. They prevent leakage of fluids and gases and maintain the integrity of the engine’s combustion chambers and other components. Gaskets are typically made of materials like rubber or metal and need to be carefully chosen to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Regular inspection and replacement of worn-out gaskets are necessary to prevent engine damage and maintain proper engine performance.
Common Issues with Manifolds and Gaskets
Over time, manifolds and gaskets can develop issues due to wear and tear, heat, and high-pressure conditions. Some common problems include manifold leaks, gasket failures, and warped or cracked manifolds. A leak in the intake manifold can result in decreased engine performance and fuel efficiency, while an exhaust manifold leak can lead to excessive noise, poor emissions, and potential damage to other engine components. Gasket failures, such as blown head gaskets, can cause coolant or oil leaks, overheating, and loss of engine power.
To prevent these issues, it is important to regularly inspect and maintain the manifolds and gaskets. This includes checking for any signs of leaks, such as fluid or gas stains, and performing proper torqueing of the manifold bolts. Additionally, using high-quality gaskets that are specifically designed for the engine and its operating conditions can help prolong their lifespan and prevent premature failure.
| Common Issues | Causes | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Manifold leaks | Wear and tear, heat, high-pressure conditions | Decreased engine performance, fuel efficiency |
| Gasket failures | Worn-out gaskets, overheating, high-pressure conditions | Coolant or oil leaks, overheating, loss of engine power |
| Warped or cracked manifolds | Overheating, high-pressure conditions | Excessive noise, poor emissions, potential damage to other engine components |
In conclusion, manifolds and gaskets are vital components of a car engine, ensuring proper airflow, combustion, and sealing. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components can help prevent issues such as leaks and failures, promoting optimal engine performance and longevity. By understanding the importance of manifolds and gaskets and addressing any problems in a timely manner, car owners can enjoy a smooth and reliable driving experience.
Cylinder Liners and Pistons
In the realm of car engines, cylinder liners and pistons play integral roles in the combustion process. Cylinder liners, also known as sleeves, are cylindrical shapes that are inserted into the engine cylinders to prevent wear and tear. Made of special alloy iron, these liners provide durability and longevity to the engine, ensuring optimal performance over time.
Working in tandem with the cylinder liners, pistons are essential components that move up and down inside the cylinder, driven by the combustion of fuel. Connected to the connecting rods, pistons transmit the force of combustion to the crankshaft, initiating the rotary motion that propels the vehicle forward.
The relationship between cylinder liners and pistons is crucial for the smooth functioning of the engine. The pistons fit tightly within the cylinder liners, creating a sealed environment for controlled combustion. As the pistons move up and down, they create a compression phase where the air-fuel mixture is compressed before ignition. This compression leads to a more efficient combustion process and ensures optimal power output.
| Cylinder Liners | Pistons |
|---|---|
| Prevent wear and tear | Move up and down inside the cylinder |
| Made of special alloy iron | Connected to the connecting rods |
| Provide durability and longevity | Transmit the force of combustion to the crankshaft |
Connecting Rods and Crankshafts
When it comes to understanding the inner workings of a car engine, it’s crucial to delve into the roles of connecting rods and crankshafts. These components play a vital part in transmitting power from the pistons to the wheels of the vehicle, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
Connecting rods, also known as conrods, serve as the link between the pistons and the crankshaft. They have a crucial role in converting the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion. Made of sturdy materials such as steel, connecting rods are designed to withstand high forces and ensure the smooth transfer of energy. They feature bearings at both ends to minimize friction, allowing for seamless movement as the pistons move up and down.
The crankshaft, on the other hand, is responsible for converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion. As the connecting rods transmit the force from the pistons, the crankshaft converts this force into rotational energy. This rotational motion is then transferred to the wheels of the vehicle, propelling it forward. The crankshaft is a robust component, often made of hardened steel, to withstand the intense forces and provide reliable performance.
Together, connecting rods and crankshafts form an integral part of the engine’s power delivery system. Their efficient operation ensures that the energy generated by the combustion process is effectively transmitted to the wheels, allowing for a smooth and powerful driving experience.
| Connecting Rods | Crankshafts |
|---|---|
| Connects pistons to the crankshaft | Converts reciprocating motion into rotary motion |
| Made of sturdy materials like steel | Often made of hardened steel |
| Features bearings at both ends for smooth movement | Designed to withstand intense forces |
| Transfers force from the pistons to the crankshaft | Transmits rotational energy to the wheels |
Understanding the functions and interactions of connecting rods and crankshafts is vital for anyone interested in the mechanics of a car engine. These components work together seamlessly to ensure efficient power delivery, resulting in a smooth and enjoyable driving experience.
As we continue exploring the various components that make up a car engine, the next section will shed light on the crucial roles of camshafts and engine valves. These components play a significant part in regulating the flow of air and fuel within the engine, contributing to its overall performance and efficiency.
Camshafts and Engine Valves
In the world of car engines, camshafts and engine valves play a crucial role in the overall functioning and performance. Camshafts are responsible for precisely opening and closing the engine valves at the correct timing, allowing the air-fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber and the exhaust gases to exit. They are connected to the crankshaft and rotate at half the speed, ensuring synchronous operation with the engine’s pistons.
The engine valves, on the other hand, act as gatekeepers. They control the flow of air and fuel into the combustion chamber and expel the exhaust gases produced during the combustion process. The valves are guided by valve guides, which help maintain their alignment and proper functioning. Engine valves are subject to high temperatures and pressures, so they must be made of durable materials that can withstand these conditions.
The interaction between the camshafts and engine valves is critical for optimal engine performance. Precise timing and synchronization ensure efficient fuel combustion, resulting in smooth and powerful engine operation. Any issues with the camshafts or engine valves can lead to reduced power, poor fuel efficiency, and even engine damage. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are essential to ensure their proper functioning and prolong the engine’s lifespan.
Table: Comparison of Different Valve Types
| Valve Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Overhead Valve (OHV) | Simple design, better low-end torque | Bulky, limited airflow |
| Overhead Camshaft (OHC) | Improved airflow, compact design | Complex timing mechanism, higher manufacturing cost |
| Double Overhead Camshaft (DOHC) | Increased power output, better control over valve operation | Higher cost, more complex maintenance |
The table above provides a comparison of different valve types commonly found in car engines. Each valve type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the engine and vehicle. It is important to consider factors such as power output, fuel efficiency, and maintenance cost when selecting the appropriate valve type for a particular engine.
Lubrication System and Oil Filter
The lubrication system plays a critical role in ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of a car engine. By providing a layer of lubrication between moving parts, it minimizes friction and reduces wear. This system consists of several components, including an oil pump, oil galleries, and an oil filter.
The oil pump is responsible for drawing oil from the oil pan and circulating it throughout the engine. It ensures that all moving parts, such as pistons, crankshafts, and camshafts, receive a sufficient supply of lubrication. Without proper lubrication, these parts would experience increased friction, leading to overheating and potential damage.
One essential component of the lubrication system is the oil filter. As the name suggests, the oil filter removes impurities and contaminants from the oil, ensuring its cleanliness and effectiveness in lubricating the engine. Over time, dirt, debris, and metal particles accumulate in the oil, which can cause damage if not filtered out. The oil filter captures these contaminants and prevents them from circulating through the engine, helping to maintain its performance and extending its lifespan.
Regular maintenance and oil changes are necessary to keep the lubrication system operating optimally. By replacing the oil and oil filter at recommended intervals, car owners can help prevent engine damage and maintain the efficiency and reliability of their vehicles. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for oil type and filter replacement to ensure proper lubrication and filtration.
Conclusion
Understanding how a car engine works is crucial for car owners and enthusiasts alike. The engine operates on the principle of internal combustion, where fuel is ignited inside the engine to generate heat and mechanical torque. By comprehending the engine’s working principle, we gain insight into the various components and their functions, enabling us to better maintain and care for our vehicles.
The engine’s parts and components, such as the cylinder block, crankshaft, and camshaft, work together harmoniously to convert fuel into mechanical energy. Each component has a specific role to play in the engine’s operation, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
As car owners, having a comprehensive understanding of our car engines allows us to make informed decisions when it comes to maintenance and servicing. By keeping our engines well-maintained and ensuring proper lubrication, we can enhance their performance, extend their lifespan, and avoid potential breakdowns.
Engine operation in New Zealand
In New Zealand, car engines operate on the same principles of internal combustion as engines worldwide. The combustion of fuel generates the power needed to move our vehicles and propel us on our journeys. By familiarizing ourselves with the working principles of car engines, we empower ourselves to make informed choices and take proper care of our vehicles.
FAQ
What is the role of a car engine in a vehicle?
The car engine is the heart of the vehicle and provides the energy needed to move the vehicle.
How does a car engine work in New Zealand?
In New Zealand, car engines operate on the principles of internal combustion, which involves the combustion of fuel inside the engine to generate heat and mechanical torque.
What are the main components of a car engine?
The main components of a car engine include the cylinder block, cylinder head, crankcase, oil pan, manifolds, gaskets, cylinder liners, pistons, piston rings, connecting rods, crankshafts, camshafts, flywheels, engine valves, governors, oil filters, distributors, water pumps, combustion chambers, timing belts, and rocker arms.
What is the function of the cylinder block?
The cylinder block is the basic framework of the engine and provides a foundation for other components. It houses the cylinders, ports for valves, and passages for cooling water circulation.
What is the purpose of the crankcase?
The crankcase is the lower part of the cylinder block and houses the crankshaft. It provides support for the main journals and bearings of the crankshaft and maintains their alignment under various engine loads.
What do the engine manifolds do?
Engine manifolds carry the air-fuel mixture and exhaust gases. The intake manifold carries the air-fuel mixture from the carburetor to the cylinders, and the exhaust manifold carries the exhaust gases from the cylinders to the exhaust system.
What are cylinder liners?
Cylinder liners, also known as sleeves, are cylindrical shapes inserted into the cylinders to prevent wear. They can be replaced when worn out and are made of special alloy iron.
How do connecting rods and crankshafts work together?
Connecting rods connect the pistons to the crankshaft and convert the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion. Crankshafts then convert the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion and transfer the energy produced by combustion to the wheels of the vehicle.
What is the role of camshafts and engine valves?
Camshafts are responsible for opening and closing the engine valves at the correct timing. Engine valves control the flow of air and fuel into the combustion chamber and the exhaust gases out of the chamber.
How does the lubrication system in a car engine work?
The lubrication system ensures that the moving parts of the engine are properly lubricated to minimize friction and wear. It consists of an oil pump that draws oil from the oil pan and distributes it to various engine components through oil galleries. The oil filter removes impurities and contaminants from the oil to maintain its cleanliness and effectiveness in lubricating the engine.
Why is it important to understand how a car engine works?
Understanding how a car engine works allows car owners to better maintain and care for their vehicles, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.




